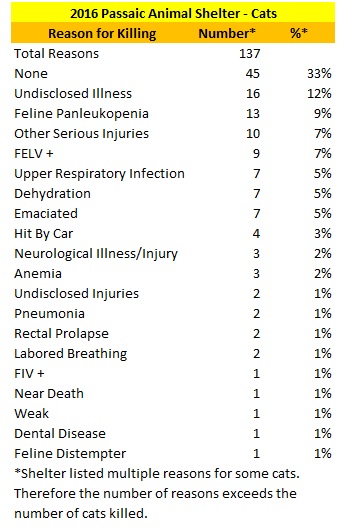
Last year, many people applauded Bloomfield’s decision to accept Bergen County Humane Enforcement’s and Bergen Protect and Rescue’s bid to run the Bloomfield Animal Shelter. After years of problems with the Bloomfield Department of Health and Human Services’ running of the animal shelter, which included banning virtually all volunteers and prohibiting a well-known trainer from keeping a dog with very minor behavioral problems, people were understandably eager to welcome an organization stating it would run a no kill shelter. Given Vincent Ascolese’s charismatic personality and him saying all the right things during a presentation to the town, one could hardly blame people for cheering Bloomfield’s decision to hire this organization.
Personally, I was very skeptical of Bergen County Humane Enforcement and North Jersey Humane Society, which was formed to run the Bloomfield Animal Shelter. First and foremost, I knew Vincent Ascolese, who is the Director of both Bergen Protect and Rescue and North Jersey Humane Society and the Supervising Animal Control Officer, previously brought animals from Hudson County to the horrific Jersey Animal Coalition. Second, Vincent Ascolese’s shelters contract with a for profit animal control company with a checkered history in Hudson County.
I was extremely disappointed when my spouse, my young child and I visited Bergen Protect and Rescue’s Cliffside Park shelter. The facility was extremely small and cramped and two people could barely pass each other through the tiny hallway inside the facility. After being ignored for 10 minutes by the the person in charge that day, we asked if we could see the dogs. This person told us no dogs were up for adoption at the facility and we had to make an appointment to see the animals even if they had any dogs up for adoption. The staff person’s claim seemed odd as many dogs were in a small area just around the corner from us. Even worse, the very next day I saw the shelter post one of the dogs I saw outside on their Facebook page as available for adoption. In addition, the staff person told us the adoption fee for an adult pit bull was over $300. While the staff person said we could drive to an adoption event the shelter was having that day, it was impractical as we did not know the area. Thus, my personal experience with this organization was not good.
Subsequently, I read about policies not consistent with well-run no kill animal control shelters. First, I saw high adoption fees on their web site (now the shelter does not even state what the fees are) which were consistent with the over $300 adoption fee communicated to us at the Cliffside Park shelter. The shelter’s web site states it may take up to a week to adopt an animal resulting in reduced lifesaving and potential overcrowding. Additionally, the Cliffside Park shelter transports many dogs in from out of state despite having what seemed like a very undersized facility. Not surprisingly, my analyses of the Cliffside Park facility’s 2013 performance showed the shelter only adopted out 35% of the number of dogs and 33% of the number of cats the shelter should adopt out. Finally, I was concerned seeing North Jersey Humane Society adopts out at least some intact animals where the shelter refers the adopter to a low cost vet clinic participating in the state subsidized spay/neuter program (funding often runs out during the year resulting in significant delays for the discounted spay/neuter services). Typically, I only see poorly run pounds use this program rather than doing the surgeries themselves with the shelter’s veterinarian. Thus, North Jersey Humane Society’s polices were not consistent with those of well-run no kill animal control shelters.
Last week’s news about the NJ SPCA charging Vincent Ascolese with animal cruelty floored me. The NJ SPCA rightfully charged Mr. Ascolese with 14 counts of animal cruelty for killing an injured deer fawn by slashing its neck with a knife and other issues with animal care at his facility. As bad as this news sounded, it paled in comparison to what I read in the recent New Jersey Department of Health inspection report of North Jersey Humane Society’s Bloomfield shelter.
Bloomfield and North Jersey Humane Society Allow Animals to Reside in a Dump
North Jersey Humane Society’s bid to perform animal sheltering services at the Bloomfield Animal Shelter required the town to bring the facility up to the standards of N.J.A.C. 8.23A. As a result, Bloomfield had a contractual obligation to ensure the building complied with the state law’s standards. Additionally, North Jersey Humane Society had a legal and moral obligation as the shelter operator to ensure the animals were housed in a safe facility.
The inspection report stated the facility was under construction and did not have the required permits. Additionally, the Bloomfield Department of Health and Human Services did not perform the required annual inspection and therefore the shelter did not have a license to operate.
The facility was occupied while under construction without evidence of local occupancy approvals and electrical, mechanical (HVAC), and building or construction permits.
The facility was not inspected by the local health authority for the current year and was not in compliance with these rules, and therefore, was not licensed at the time of this inspection.
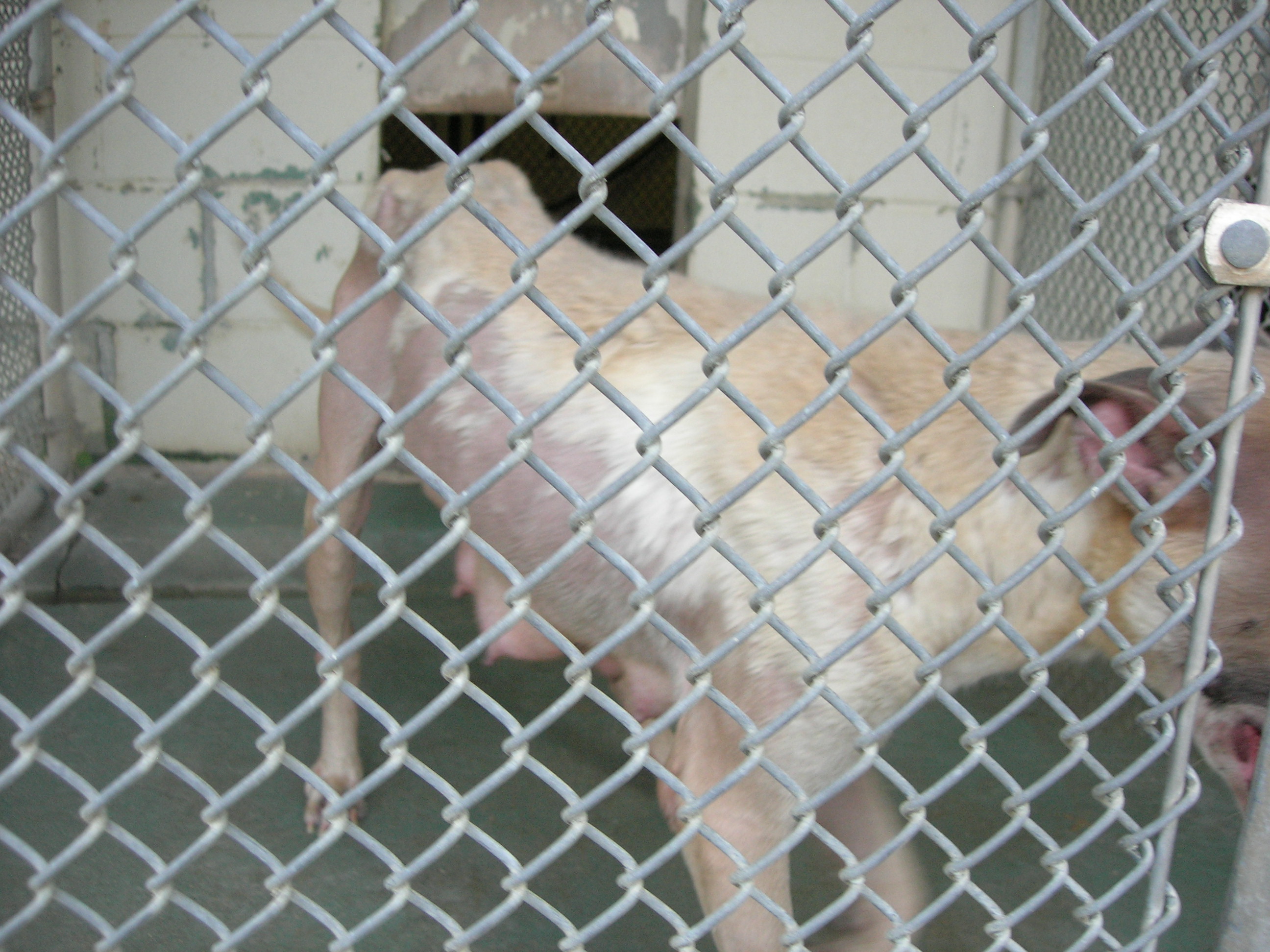
Despite the shelter having many unsafe areas, North Jersey Humane Society housed animals in these conditions. The shelter kept dogs in a room without a ceiling with uncovered electrical wires and various dangerous items were hanging down from above.
The ceiling of the guillotine room was removed and was completely open to the rafters in the attic space. Dogs were being housed in this room at the time of this inspection. Electrical wires and junction boxes were exposed and hanging and were not properly secured as required; insulated ventilation ducts and other items were exposed and hanging down from the rafters (Pictures 2834 through 2836).

North Jersey Humane Society left exposed screws adjacent to dog enclosures and the shelter’s entrance putting both people and animals at risk of injury.
There were boards with long protruding screws located on the ground near the entrance gate of the facility adjacent to an outdoor animal enclosure. These screws could cause injury to both animals and people (Picture 2829).

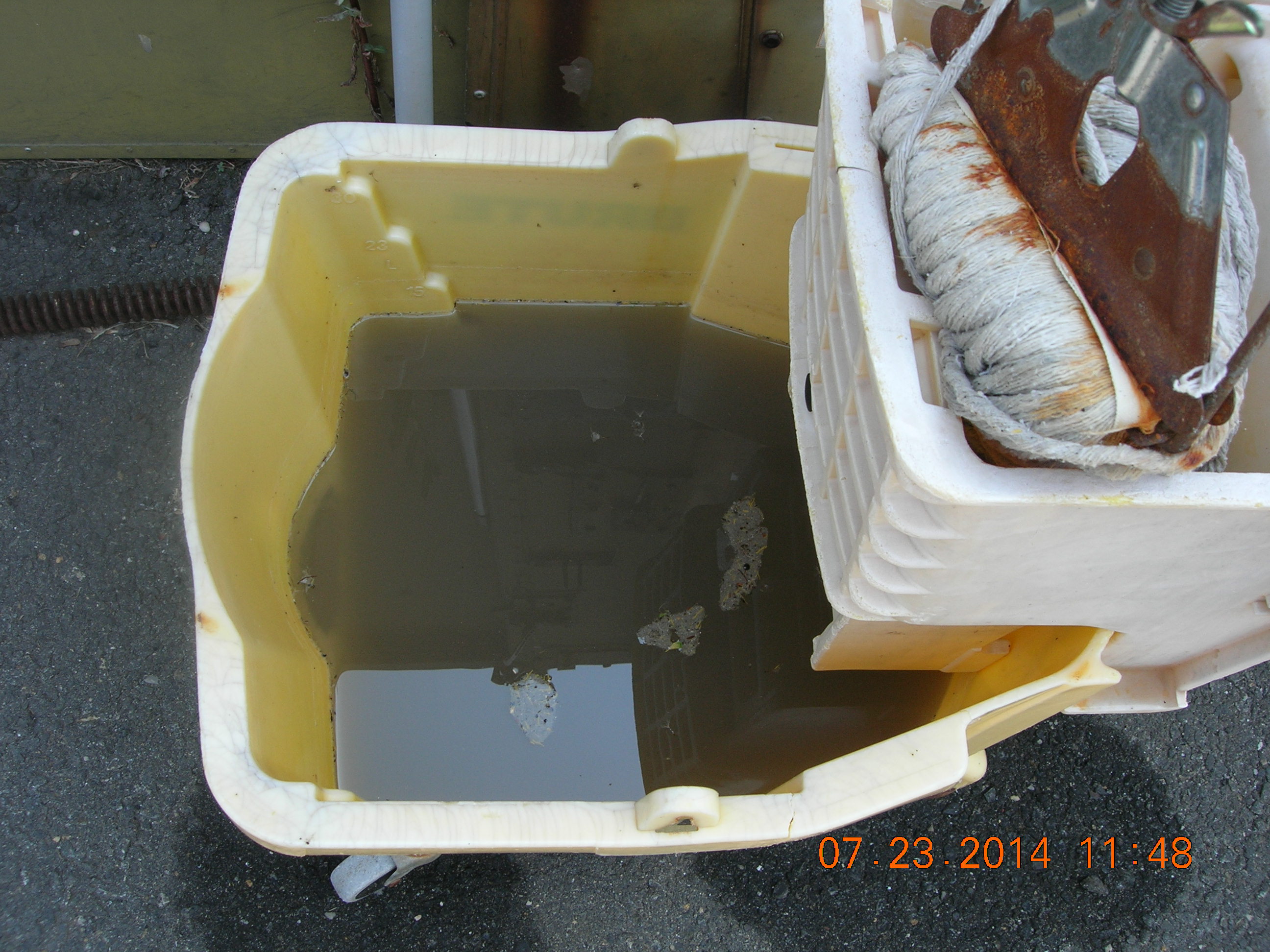
The shelter had inadequate ventilation and smelled like urine. Furthermore, insufficient lighting prevented shelter staff from properly cleaning the animal enclosures resulting in a build up of feces and urine. North Jersey Humane Society apparently placed an outdoor animal enclosure on a surface that shelter staff cannot effectively disinfect. Furthermore, the town and North Jersey Humane Society did not repaint the surfaces of the outdoor animal enclosures and the staff could therefore not properly clean these kennels.
There was a strong, stale urine odor in the first animal enclosure room located next to the main office of the facility at the time of this inspection; the ventilation was not sufficient to remove odors as required.
The lighting in the facility was not sufficient to allow the viewing of all the interior surfaces of the animal enclosures to ensure that the enclosures had been cleaned and disinfected. The enclosures in the first animal enclosure room contained small pools of urine and small fragments of feces in the corners and bottom edges that had not been removed during the cleaning process. These corners and edges were unable to be viewed clearly due to the insufficient distribution of lighting in this room.
There was a chain link enclosure placed on the pavement in the driveway in front of the facility. This asphalt pavement was not impervious to moisture and not able to be readily cleaned and disinfected. This enclosure did not have any drains to contain and properly dispose of run off as required (Picture 2831).
The surfaces of the outdoor animal enclosures attached to the side of the building and accessible to the animals in these enclosures by a guillotine door were not impervious to moisture. These surfaces were originally painted, but the paint was peeling, and the surfaces were no longer impervious to moisture (Picture 2844).


North Jersey Humane Society housed dogs in dangerous enclosures posing a risk of injury and possible death. The shelter left one dog in an outdoor enclosure without sufficient shade for two hours on a hot day in August and the inspector observed the dog drooling. Furthermore the dog bed in this enclosure was broken and had sharp exposed points. Another dog named Benny had a sharp metal wire that was in his cage.
The outdoor dog enclosure on the concrete slab in the driveway next to the entrance gate of the facility had a tarp type of material strapped to the top of the enclosure, but this tarp was not suitable to provide sufficient shade to avoid overheating or discomfort of the animals housed in this enclosure. ACO Stewart stated that the dog housed in this enclosure at the time of this inspection had been in the enclosure approximately two hours and the dog’s drooling was normal and not caused by overheating (Picture 2828).
A dog bed located in an outdoor enclosure near the entrance gate of the facility was broken and in need of repair. The bed contained metal triangle screw plates that had become separated from the frame. The points of the plate were exposed in an upward position and the legs of the bed were bent over (Picture 2828).
A small, thin, red coated dog named Benny was housed in an upper level enclosure in the annex room. The door of the enclosure had a wire that was bent over and protruding into the enclosure at the level of the dog that could cause injury (Picture 2856).


To make matters worse, the shelter housed two large Rottweilers in kennels that were approximately 30% smaller than required by N.J.A.C. 8.23A 1.6 (b):
Two large Rottweilers at the facility at the time of this inspection were each housed in primary enclosures that provided approximately 10.34 square feet of floor space when measured from the inside of the enclosure. These dogs were estimated to be approximately 39 to 42 inches long and required approximately 14 to 16 square feet of floor space.
North Jersey Humane Society Fails to Properly Clean its Shelter
North Jersey Humane Society failed to use proper procedures to clean the shelter. Specifically, the shelter did not remove cat litter, hair and other debris from an enclosure holding multiple cats. The shelter did not use EPA registered cleaning products. Even worse, the facility did not have suitable measuring devices to ensure staff applied the proper concentration of disinfectants.
Cats were being placed in a three tier cat cage during the daily cleaning process. This enclosure was being sprayed down with a spray bottle and immediately wiped out with a towel between each cat, but this cage was not being disinfected as required. There was an accumulation of cat litter, hair, and other debris trapped in the wire along the edges of the resting benches and at the bottom of this wire enclosure that had not been removed, cleaned and disinfected between each cat during the cleaning process. Toys were also being sprayed with the contents of the spray bottle and immediately wiped off, without allowing the required contact time for disinfection.
The bleach that was being used on the day of this inspection was Clorox Scented, Spashless bleach, which is not an EPA registered disinfectant. Two small bottles of Clorox regular bleach were later found in the upstairs storage area.
The disinfectants used at the facility, sodium hypochlorite (chlorine bleach) and Accel (accelerated hydrogen peroxide), were not being used at the correct dilution for disinfecting animal contact surfaces. The Accel requires a dilution ratio of 8 ounces (one cup) per gallon of water and the chlorine bleach that was found in the upstairs storage area requires 4 ounces (one half cup) per gallon of water according to the instructions on the product labels for disinfection of smooth and impervious animal contact surfaces.
There were no suitable measuring devices being used at the time of this inspection. One capful of these products (said to be approximately one ounce of concentrated solution) was being mixed into a one and a half gallon sprayer that was labeled as “Bleach” (Picture 2857). The cages were said to be sprayed down with this solution, allowed to sit for approximately 10 minutes while other cages are being sprayed down, and then the cages are rinsed with a hose and the remaining water was removed with a squeegee. The cages were not manually scrubbed clean at any time during the cleaning process.

Furthermore, shelter staff stated they cleaned animal enclosures, but the inspector’s tape measure became covered with urine and feces when she was examining the cages.
The animal enclosures located in the first room of the facility near the office and main entrance to the facility were said to have been cleaned, but when a metal tape of a tape measure was placed in one of the upper cages while measuring the cage size, the length of tape became contaminated with urine and small bits of feces that remained inside of the cage after the cleaning process. The facility staff was not following proper cleaning and disinfection procedures to reduce disease hazards and odors caused by bacteria and other contaminants that remained on animal enclosure surfaces.
Finally, North Jersey Humane Society failed to use a proper cleaning solution to disinfect the animals’ food and water receptacles.
Food and water receptacles were being washed with a dishwashing liquid, rinsed and placed on a towel to dry, but they were not being disinfected daily as required. ACO Ascolese stated over the phone on the day of this inspection that the receptacles were being washed with an antibacterial type hand dishwashing liquid, but this type of dishwashing liquid was not an EPA registered disinfectant for use in animal facilities.
Cruel Treatment of Wildlife
North Jersey Humane Society treated wildlife in a way that constituted animal cruelty in my view. Two days prior to the inspection, the shelter impounded a 3 week old baby squirrel that was too young to eat, drink, urinate and defecate on its own. Instead of bottle-feeding this animal or sending the animal to a licensed wildlife rehabilitation center, the shelter tried to feed the animal with a honey seed stick. The inspector told both the ACO at the shelter and Vincent Ascolese that the shelter must transport the squirrel to a licensed wildlife rehabilitation center immediately. Furthermore, a New Jersey Division of Fish and Wildlife agent also stated the squirrel needed to go to a licensed wildlife rehabilitation center right away. Despite this emergency, Vincent Ascolese refused to do so and said he’d take the animal to the animal hospital the shelter uses.
Frankly, I am appalled that the shelter does not take injured wildlife to licensed wildlife rehabilitation centers. Even some very regressive kill shelters transport wild animals to these facilities. Furthermore, North Jersey Humane Society and Bergen Protect and Rescue could have made a simple plea on their social media pages and many people would have gladly transported the animal and offered monetary assistance.
To make matters worse, the baby squirrel and an iguana were housed in the feral cat room where the door is left open overnight. The inspection report noted some type of animal entered the room as evidenced by feces found in one of the cages. Additionally, the bars in the baby squirrel’s cage were wide enough for the animal to fall through. Given the young squirrel had not yet opened its eyes, this was a very real possibility. In fact, this did happen and the inspector actually caught the baby squirrel falling from its cage. Furthermore, the shelter staff left water in a bowl for the baby squirrel that was deep enough for the animal to drown in. As a result, the baby squirrel was housed in a room with potential predators, feral cats and wildlife that could enter the room, and left in an environment where it could drown or even fall to its death.
A baby squirrel that was impounded at the facility on 8/17/15 was crying in distress in search of its mother at the time of this inspection. This squirrel was approximately 3 weeks old and was too young to eat, drink and eliminate on its own and at this young age, may have been unable to regulate its body temperature. This squirrel was not receiving proper care and nourishment as required and was not placed in a suitable housing environment to maintain the safety and wellbeing of this animal for the two days that it was housed at the facility (Pictures 2849 and 2850).


A baby squirrel, approximately 3 weeks of age with its eyes not yet open, that was impounded at the facility on 8/17/15 was not being fed as required to meet the nutritional needs of this young squirrel. There was no infant replacement formula of any kind or any electrolytes or other preparation for rehydration at the facility for this squirrel at the time of this inspection.
The baby squirrel detailed in 1.7 (b) was not fed or provided with a rehydration solution during the entire inspection period. A squirrel of this age requires feeding approximately every three hours.
ACO Stewart stated that George, who was not at the facility at the time of this inspection, had been feeding the squirrel seeds and honey on a stick. Although the squirrel was too young to forage, the staff had placed the honey seed stick in the red cedar chip bedding with the assumption that the squirrel would search for its food.
The inspector, Frese, explained to ACO Stewart that this squirrel was a nursing squirrel and was too young to eat, drink, and eliminate on its own. Frese stated that this squirrel needed to be transported to a licensed wildlife rehabilitator immediately. ACO Stewart stated that the squirrel could not be transported at that time, but would be transported the next day. Frese stated that the squirrel may not live that long and then called the New Jersey Division of Fish and Wildlife and the New Jersey Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (NJSPCA) for assistance. Neither agency was available to transport the squirrel; the agent from the Division of Fish and Wildlife said the squirrel needed to be transported immediately to a licensed wildlife rehabilitator.
The Supervising ACO, Vincent Ascolese, called and spoke to Frese on the phone and explained that the squirrel was being cared for adequately with the seed stick placed in the bedding to teach the squirrel to find its food. Frese explained again that the squirrel was too young to forage and needs to be transported immediately to a rehabilitator. ACO Ascolese stated that they do not take any wildlife to a wildlife rehabilitator. He stated that he would instruct the staff to take the squirrel to Franklin Lakes Animal Hospital; that is where they take all injured and orphaned wildlife. ACO Ascolese stated that it is their policy for all injured and orphaned wildlife to be transported directly to the Franklin Lakes Animal Hospital, Wildlife Division.
There was a hole in the ceiling of the room named the “feral cat” room (Picture 2851) and the animal control officer (ACO) Nicole Stewart, confirmed that the door to this room had been left open to the outside of the building overnight. There were feces in one of the cages in this room from some type of animal that had entered the room and perched on the top of the cage (Picture 2848). An iguana and a baby squirrel were housed in this room at the time of this inspection and had been in the room while the door was open overnight. ACO Stewart stated that this room is used for the feral cats that free roam the grounds of the facility.


A baby squirrel was housed in an enclosure that had bars on the enclosure door that were wide enough for the squirrel to fit through. The squirrel was too young to walk normally, but was able to crawl. The squirrel crawled to the front of the enclosure and fit itself through the bars of the door. The squirrel had come halfway out of the enclosure, but was caught by the inspector, Frese, before it fell and was placed into the back into the enclosure. The squirrel was vocalizing a distress call as it crawled out of the cage (Picture 2866).

The baby squirrel that was too young to eat and drink on its own was provided with a straight sided bowl filled with water in the enclosure that was deep enough that the squirrel could have become trapped and drowned in the water, due to the age and inadequate mobility of the squirrel.
The inspection report documented Vincent Ascolese killing an injured deer fawn. North Jersey Humane Society picked up a deer fawn with two broken legs in Woodland Park 12 minutes after the animal hospital the shelter uses closed (the animal hospital’s web site currently states it is open on the day of the week and time this happened). Instead of immediately taking the injured deer to another animal hospital or better yet, a licensed wildlife rehabilitation facility, as required by law, North Jersey Humane Society brought the animal back to the Bloomfield shelter. Vincent Ascolese subsequently slashed the deer’s throat in what one could consider an audition for joining the terrorist group, ISIS. Irregardless of whether the animal was hopelessly suffering, the shelter was required to send this animal for veterinary treatment. Even if euthanasia was required, slashing a deer’s throat is not humane and is illegal in New Jersey. Thus, Vincent Ascolese acted in an illegal and unethical manner and is now rightfully charged with animal cruelty.
A deer that was picked up by ACO McGowan in Woodland Park, Passaic County, on 6/29/15 was described on the “Animal Control Incident Transport Record” form as being severely injured and bleeding, with both hind legs broken and bone protruding through skin. The form stated “Well Pet Animal Hospital closed.” According to the website for this animal hospital, the normal business hours on Mondays, the day of the incident, are 9 AM to 6 PM. According to the animal control incident form, the ACO had arrived at the scene of the severely injured deer (fawn) at 6:12 PM, which was outside of this hospital’s posted hours of operation. The deer was transported to the Shelter facility at 6:47 PM. The “Animal Control Incident Transport Record” form indicated that the ACO did not immediately obtain emergency veterinary care from a licensed veterinarian as required by this regulation.
ACO Ascolese, stated during a phone call at the time of this inspection, that it is their policy for all injured and orphaned wildlife to be transported directly to the Franklin Lakes Animal Hospital, Wildlife Division. The severely injured deer that was picked up on 6/29/15 was not transported to the Franklin Lakes Animal Hospital in accordance with the policy stated by ACO Ascolese. The website for the Franklin Lakes Animal Hospital shows that the hospital’s regular operating hours are from 9 AM to 8 PM on Mondays.
A deer (fawn) that was impounded at the facility on 6/29/15 was killed by ACO Ascolese who cut the throat of the deer with a knife resulting in exsanguination (death from loss of blood). Exsanguination is an unacceptable method of euthanasia in accordance with these regulations.
Furthermore, even if throat slashing was a legal euthanasia method, Vincent Ascolese was not allowed to euthanize animals under state law at that time since he lacked the certification to do so.
Dr. Diaz confirmed that he had certified ACO Ascolese in August, 2015. On 6/29/2015, ACO Ascolese killed a deer (fawn), prior to the animal euthanasia training that had been conducted on or about 8/12/2015.
North Jersey Humane Society Fails to Provide Adequate Care to its Animals
The shelter did not provide prompt veterinary care to an injured dog. Benny had open sores on his legs and was not placing any weight on his left front leg during the inspection. Despite these issues, North Jersey Humane Society provided no veterinary care for the 3 days he was at the shelter before the inspection.
A dog named Benny was not placing any weight on his left front leg at the time of this inspection. This dog also had several ulcer type sores in various locations on all four of his legs, most of which were covered with smooth, hairless, blackened skin tissue with a raised outer edge, but some of these sores were shallow open wounds with a red and pink wound bed. This dog had not received any veterinary care since it arrived at the facility on Sunday, August 16, 2015 (Picture 2856).

North Jersey Humane Society also did not provide some animals adequate amounts of water. Specifically, an iguana had no water during the 7 hour inspection and the inspector had to tell shelter staff to provide water to a thirsty Rottweiler.
An iguana located in the feral cat room had spilled its water and the water had not been replaced during the inspection.
A Rottweiler that was housed in an outdoor enclosure did not have water in his water bucket at the time of this inspection. This dog was subsequently provided with water after this was brought to the attention of ACO Stewart (Picture 2868 through 2870).


Shelter staff also left an iguana to sit in a wet bed during the entire 7 hour inspection.
An iguana that was impounded at the facility on 8/17/15 was housed in an enclosure with wet bedding after the water from the water bowl had been spilled in the enclosure. This wet bedding had not been changed during the entire inspection period (Picture 2867).

North Jersey Humane Society did not isolate sick animals from healthy animals. The facility’s HVAC system emitted air from the isolation area, which is supposed to house sick animals, to locations holding healthy animals. In fact, the shelter used the ineffective isolation area it did have to house four healthy dogs due to overcrowding. And just how did the shelter become overcrowded? The facility transported 15 dogs, which made up 60% of the facility’s dog population at the time of the inspection, from Georgia 3 days before.
The facility did not have any isolation procedures in place and did not have a proper isolation area at the time of this inspection.
The ventilation in the dog and cat isolation rooms was not separated from the air used for the general population. The ventilation for the isolation rooms was supplied through the HVAC system for the facility and mixed with the air for the general population and did not exhaust directly to the outdoors as required.
Due to lack of space, the dog isolation room was being used to house 4 healthy dogs at the time of this inspection and the cat isolation room housed 13 cats that were not exhibiting signs of or being treated for a communicable disease. The dog isolation room did not have floor to ceiling walls and was open at the top of the walls to the holding area of the general dog population. The cat isolation room had windows that were open to the room where the general cat population was housed (Pictures 2861 and 2865).


The 15 dogs that had been imported from Georgia and arrived at the facility on Sunday, 8/16/15, did not have completed cage cards as of the date of this inspection.
The shelter also did not answer its supervising veterinarian’s requests going back as far as five months to acquire medicines and diagnostic equipment to treat sick and/or injured animals.
A notebook was located on the premises that showed the supervising veterinarian’s findings along with the veterinarian’s signature and date of each visit. The notes in this log book indicated that the veterinarian had recommended the pharmacy stock at the facility be increased (this would require prescriptions from the supervising veterinarian with the required prescribing information) and suggested medical and diagnostic equipment be purchased for use at the facility. These notations had been recorded in the log book since March of 2015, with the last request for equipment dated 8/2/15. The facility did not have the diagnostic equipment on the premises as requested by the supervising veterinarian.
North Jersey Humane Society also had drugs without required information, such as the animal it was prescribed for, directions for use, date dispensed, and name of the facility distributing the medication. This raises serious questions as to whether the shelter illegally obtained these medicines and whether expired drugs were given to animals.
There were medications at the facility that did not contain prescription labels with the required information, including the animal’s name or identification, directions for use, the date dispensed, and the name and license number of the licensee and facility dispensing the medication. A 200 ml bottle of Toltrazuril, used for the treatment of coccidia in horses, was located on the top of a cart in the medical treatment room. The manufacturer’s label on the bottle stated to refrigerate after opening and expires one year after opening, but the bottle was not refrigerated and there was no date on the bottle indicating when the bottle had been opened. There were no records or directions from the supervising veterinarian indicating what the medication was to be used for and to which animal it had been prescribed. There was also a box of MilbeMite brand ear mite medication for cats on this cart with no prescription label, animal identification, and instructions for use (Pictures 2871 through 2873).



North Jersey Humane Society’s Euthanasia Statistics May Not Be Accurate
North Jersey Humane Society reported it only euthanized one cat and three dogs died or went missing in its 2014 Shelter/Pound Annual Report. However, the inspection report noted 4 dead animals were in the facility’s freezer. To make matters worse, the shelter could not produce accurate and legally required intake and disposition records at the time of the inspection. Furthermore, Vincent Ascolese, who illegally killed the fawn, conveniently removed all the wildlife intake and disposition records and stored them in another county. As a result, I have no confidence in North Jersey Humane Society’s reported euthanasia and other statistics since the shelter could not produce the supporting documents.
There were also approximately four animals in the freezer that were bagged, but the bags were not labeled with a name or ID number.
Paper records were maintained on dogs and cats that were received at the facility, but the intake and disposition log which correlates when each animal arrived at the facility and the final disposition was maintained as a computer record. There was no one at the facility at the time of this inspection that had access to the computer records to ascertain when animals were received and the final dispositions. A notebook that was labeled “stray animal log” was not up to date and did not include all animals that were received at the facility. The log only listed dogs that had been impounded and the last entry was dated 7/1/15.
The “Animal Control Incident Transport Record” forms, which were the only records created for the intake and disposition of certain wildlife or other species of animals received at the facility, including the deer that was received at the facility on 6/29/15, were not kept at the premises. Kristi, the Executive Director of Shelter Services stated during a telephone conversation at the time of this inspection that all animal control records were removed from the establishment by ACO Ascolese and stored in an office located in different county.
No People Admit to Euthanizing Animals
The inspection report documented the supervising veterinarian contradicting the shelter’s statement about who performs euthanasia. Specifically, the ACO on staff during the inspection stated Dr. Nelson Diaz performs all euthanasia procedures for the shelter’s animals. However, the veterinarian stated he never euthanized any animals from the shelter despite the shelter reporting 1 euthanized cat in 2014 and four dead animals in shelter’s freezer at the time of the inspection.
Furthermore, the shelter had no required euthanasia equipment at the facility or documentation that any shelter staff were certified to euthanize animals. As a result, one has to wonder if Vincent Ascolese or some other people at the shelter illegally killed animals like Vincent Ascolese did with the deer fawn.
At the time of the inspection, no certification documents were found on the premises or made available to the inspectors to indicate which staff members were certified by a licensed veterinarian to perform humane euthanasia at the facility. ACO Stewart stated at the time of this inspection that all animal euthanasia was performed by the supervising veterinarian, Dr. Diaz. Dr. Diaz was contacted by phone and confirmed that he had not performed any animal euthanasia for this facility and he was not contacted regarding the deer (fawn) that was killed by ACO Ascolese. ACO Stewart also stated that ACO Ascolese was trained by Dr. Diaz to euthanize animals at the facility one week prior to the inspection (8/12/2015). Dr. Diaz confirmed that he had certified ACO Ascolese in August, 2015. On 6/29/2015, ACO Ascolese killed a deer (fawn), prior to the animal euthanasia training that had been conducted on or about 8/12/2015.
None of the required euthanasia equipment was on the premises at the time of this inspection; there were no posted instructions, and no euthanasia, tranquilizing or immobilizing agents on the premises. This facility was not equipped with the supplies to perform humane euthanasia on any animals at the time of this inspection and there were no records or other evidence provided at the facility during this inspection to indicate that the facility was equipped as required to perform euthanasia on 6/29/2015 when the deer (fawn) was killed by ACO Ascolese.
North Jersey Humane Society Violates Basic No Kill Principles
No kill shelters essentially need to do three broad things. First and foremost, no kill sheltering mandates not killing or allowing healthy and treatable animals to die. Second, no kill facilities must perform at a high level resulting in animals quickly leaving the shelter and going to good homes. Third, no kill sheltering requires animals be provided with an elite level of care.
North Jersey Humane Society violated all three of these principles. Vincent Ascolese never even tried to get the injured fawn to a licensed wildlife rehabilitation center. In fact, Mr. Ascolese’s organization does not use licensed wildlife rehabilitation centers for any wild animals per the inspection report. His shelter’s careless disregard for an extremely vulnerable baby squirrel also violated no kill’s unwavering standard of not killing. Whether the shelter killed the baby squirrel directly or simply allowed it to die makes no difference. The shelter must have a passion for saving animals. Clearly, Vincent Ascolese’s organization has an attitude that some animals are simply not worth saving. After all, when the Director of North Jersey Humane Society slices open the throat of a fawn, is it any wonder other staff members will not do anything to save a baby squirrel?
North Jersey Humane Society’s and Bergen Protect and Rescue’s polices resulting in prolonged lengths of stay also violate no kill principles. To make a no kill animal control shelter work, the organization must quickly place animals into good homes. With excessive adoption fees, long waiting periods to adopt animals and poor customer service, Vincent Ascolese’s shelters simply do not perform in the manner they should.
Finally, North Jersey Humane Society fails to follow basic animal sheltering practices let alone the elite level standards of a no kill facility. Housing sick animals together, leaving animals without water, not providing prompt veterinary care, keeping animals in filthy enclosures, exposing animals to dangerous kennels, and potentially providing animals with expired medicines is unacceptable for any shelter, kill or no kill. Clearly, North Jersey Humane Society failed its animals and does not deserve the no kill or even a shelter label.
Bloomfield Needs to Take Immediate Action
Bloomfield and the shelter’s other contracting municipalities should expect far better service. Assuming North Jersey Humane Society’s annual fees are the same as its $120,000 bid for animal control and $145,000 bid for sheltering services, North Jersey Humane Society receives $265,000 a year in revenue from these towns. Based on the Bloomfield Animal Shelter’s total reported intake in 2014, this works out to nearly $1,500 of revenue per animal the shelter impounds. Also, the shelter receives donations in addition to these contract fees. Surely, North Jersey Humane Society can afford to provide proper care to its animals.
Bloomfield no longer can trust Vincent Ascolese to do the right thing. First, Bloomfield must make all necessary structural improvements to the shelter to ensure the facility can comply with state law. Second, the town must form an Animal Welfare Advisory Committee, which should have qualified members dedicated to ensuring the town has an elite no kill shelter and to oversee and regulate whoever runs the Bloomfield Animal Shelter. Third, Bloomfield must enact the Companion Animal Protection Act (“CAPA”) that residents have demanded for years. Fourth, the town should pass a no kill resolution mandating at least a 95% live release rate for dogs and a 90% live release rate for cats impounded from the towns the shelter contracts with. Fifth, the town should demand North Jersey Humane Society stop transporting animals from southern states into the Bloomfield Animal Shelter. Simply put, the town can no longer take the word of a charismatic person with a dark side.
New Jersey Department of Health, the NJ SPCA and the Towns Contracting with Bergen Protect and Rescue Must Investigate That Shelter
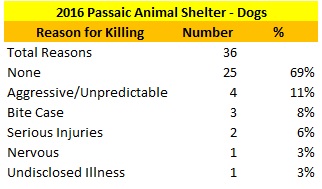
Based on the egregious performance of North Jersey Humane Society, the New Jersey Department of Health and NJ SPCA must investigate Bergen Protect and Rescue to see if Vincent Ascolese’s other facility is also violating New Jersey shelter and animal cruelty laws. Furthermore, Cliffside Park should also do the same things as I recommend for Bloomfield to ensure the shelter is effectively supervised and regulated. Sadly, Vincent Ascolese’s organizations have lost all credibility and it is time these shelters prove to everyone they are ready to step up their game. If not, then the municipalities must move on and bring an organization in that will do the right things for the animals.




































 As I mentioned in my blog last year,
As I mentioned in my blog last year, 









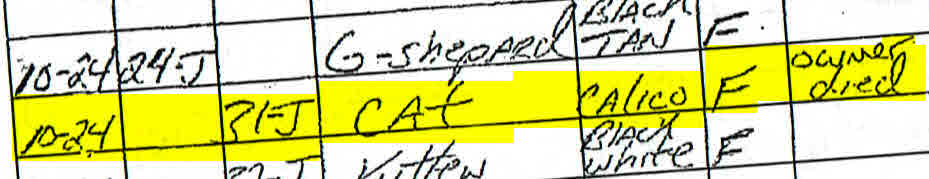
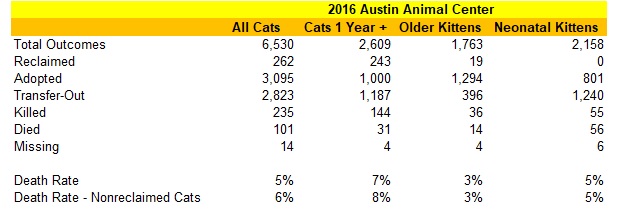
 Cat 12-L was a 10 year old cat taken to the Elizabeth Animal Shelter on December 14, 2016 by the property managers of an apartment complex. Presumably, this cat lived in a home, perhaps in one of the apartments in this building, since the property managers noted the cat was house trained. Despite this fact, the Elizabeth Animal Shelter killed this older cat for being feral and aggressive a little after a month later.
Cat 12-L was a 10 year old cat taken to the Elizabeth Animal Shelter on December 14, 2016 by the property managers of an apartment complex. Presumably, this cat lived in a home, perhaps in one of the apartments in this building, since the property managers noted the cat was house trained. Despite this fact, the Elizabeth Animal Shelter killed this older cat for being feral and aggressive a little after a month later.